This is the first issue of the newsletter I’ve kickstarted for insights into the backend engineering space encircling topics like distributed systems, databases, data engineering, system design, architecture, scalability and the like, also the latest tools and technologies in the space. To get the content delivered to your inbox, you can subscribe to the newsletter at the end of this post.
Distributed Task Scheduling with Akka, Kafka and Cassandra at PagerDuty
PagerDuty, in a series of blog posts (Part 1, part 2 and part 3), discussed how they developed an open-source library with Akka, Kafka and Cassandra to solve the problem of task scheduling in a distributed infrastructure.
Their engineers needed to ensure that the tasks they schedule run on time in an orderly fashion in their infrastructure. The issue was that these tasks were arbitrary chunks of code (written to send an SMS or communicate with a database, etc.) that generally had to be scheduled at random times (one minute from now or one year from now).
If a task is scheduled to be one year from now, the infrastructure would possibly change. This would make the tasks either fail or behave in an uncertain way.
Initially, they used a solution called WorkQueue that leveraged an Apache Cassandra partitioned queue (which is an anti-pattern) to distribute tasks. The only way to execute tasks was to poll the Cassandra queue partitions. The team had to ensure all the partitions were regularly polled to maintain the task execution throughput. If a service instance polling the queue went down it required a complex sequence of steps to be replaced. Also, the WorkQueue was quite slow.
To tackle the issues, they developed a solution called the Scheduler, written in Scala. It uses Cassandra for task persistence, Apache Kafka to handle task queuing and partitioning and Akka to handle concurrency.
Redis Stack
Redis Stack clubs several Redis modules such as Redis search, Redis JSON and more in a single product to simplify the developer experience when working with various Redis modules.
Redis stack supports modern data models and data processing capabilities such as search, document, graph, time series, and probabilistic data structures—all implemented as dedicated Redis modules. In addition to this, it also provides an efficient tool to visualize and optimize Redis data.
With Redis Stack, developers can: index and query Redis data, perform full-text search, run aggregations and advanced vector similarity searches, manage time-series data, leverage graph data models and manage JSON documents efficiently.
HarperDB: More than Just a Distributed Database
With HarperDB, devs can define their own API endpoints with custom functions without having to manage the backend server. The ability to use custom functions makes HarperDB a distributed application development platform as opposed to just being a distributed database. So, as opposed to business logic residing on a dedicated backend server, it moves on to a custom function (like AWS Lambda functions).
This is something along the lines of what Firebase offers. What is different?
HarperDB is cloud platform agnostic. It can be deployed on the Edge, on-prem or used as a managed service. It can be deployed on devices as small as microprocessors like Raspberry Pi.
As opposed to traditional replication, it uses a pub-sub replication model to move data across instances within the network, ensuring we’re only moving the data we need.
LSM Tree: Data Structure Powering Write Heavy Storage Engines
Most of the leading databases leverage the B-Tree data structure for storage. But in the case of high-frequency writes accessing random nodes in the tree for updates due to the balancing operation of the tree can result in a bottleneck.
To overcome this, databases such as Cassandra and HBase leverage the Log-Structured Merge Tree or LSM for short to tackle high-frequency writes. Read on….
Directus – Open Source Data Platform
Directus is an open-source data platform that helps us visualize the data stored in our SQL databases better. Existing database tools like MySQL Workbench, phpMyAdmin and the like help visualize data, but they are more catered towards the technical folks with extensive knowledge of relational databases and SQL.
Directus is a data platform that sits on top of a SQL database (mirroring the content and the schema), providing a data toolkit for engineers as well as business people. Once configured, we immediately get a dynamic API (REST and GraphQL) and a no-code app to manage and view our data. No need to write any backend solely to fetch the data to the UI. Also, since the data is mirrored, the original data stays unaltered.
If you found the content interesting, consider subscribing to my newsletter to get the content delivered right to your inbox and share it with your network.
Shivang
Related posts
Zero to Software Architecture Proficiency learning path - Starting from zero to designing web-scale distributed services. Check it out.
Master system design for your interviews. Check out this blog post written by me.
Zero to Software Architecture Proficiency is a learning path authored by me comprising a series of three courses for software developers, aspiring architects, product managers/owners, engineering managers, IT consultants and anyone looking to get a firm grasp on software architecture, application deployment infrastructure and distributed systems design starting right from zero. Check it out.
Recent Posts
- System Design Case Study #5: In-Memory Storage & In-Memory Databases – Storing Application Data In-Memory To Achieve Sub-Second Response Latency
- System Design Case Study #4: How WalkMe Engineering Scaled their Stateful Service Leveraging Pub-Sub Mechanism
- Why Stack Overflow Picked Svelte for their Overflow AI Feature And the Website UI
- A Discussion on Stateless & Stateful Services (Managing User State on the Backend)
- System Design Case Study #3: How Discord Scaled Their Member Update Feature Benchmarking Different Data Structures
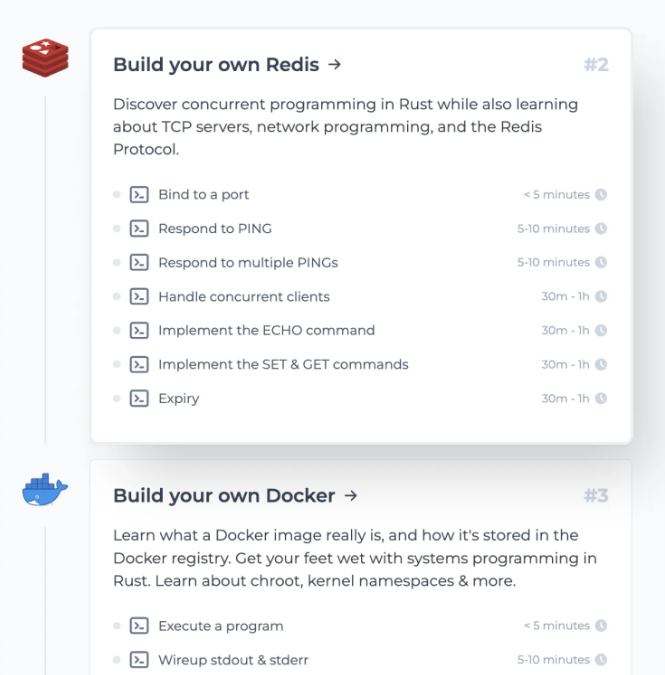
CodeCrafters lets you build tools like Redis, Docker, Git and more from the bare bones. With their hands-on courses, you not only gain an in-depth understanding of distributed systems and advanced system design concepts but can also compare your project with the community and then finally navigate the official source code to see how it’s done.
Get 40% off with this link. (Affiliate)

Follow Me On Social Media